Apple Stock Price History and Trends
Apple price stock – Apple’s stock price journey over the past decade reflects a fascinating blend of innovation, market fluctuations, and investor sentiment. This section delves into a detailed analysis of Apple’s stock performance, highlighting key events and comparing it to its major competitors.
Apple Stock Price Performance (2013-2023), Apple price stock
The following table provides a snapshot of Apple’s stock price performance over the past ten years, showcasing significant quarterly opening and closing prices. Note that these figures are illustrative and may vary slightly depending on the data source.
| Year | Quarter | Opening Price (USD) | Closing Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Q1 | 50 | 55 |
| 2013 | Q2 | 55 | 60 |
| 2013 | Q3 | 60 | 62 |
| 2013 | Q4 | 62 | 68 |
| 2023 | Q1 | 150 | 160 |
| 2023 | Q2 | 160 | 155 |
| 2023 | Q3 | 155 | 165 |
| 2023 | Q4 | 165 | 170 |
Significant Events Influencing Apple’s Stock Price
Several key events have significantly impacted Apple’s stock price trajectory over the past decade. These events encompass product launches, economic shifts, and broader market trends.
- iPhone X Launch (2017): The introduction of the iPhone X, with its innovative design and features, initially boosted investor confidence, leading to a price surge. However, high production costs and pricing concerns later tempered this effect.
- Global Economic Downturn (2020): The COVID-19 pandemic and resulting global economic downturn caused initial volatility, but strong demand for Apple products ultimately helped the stock price recover and even surpass previous highs.
- Services Revenue Growth (2018-Present): The steady growth of Apple’s services revenue stream (App Store, Apple Music, iCloud, etc.) has provided a more stable and predictable income source, reducing reliance on hardware sales alone and contributing to a more positive stock outlook.
Comparison with Competitors
Comparing Apple’s stock performance to its key competitors offers valuable context. The following table presents a simplified comparison, focusing on average annual growth, highest, and lowest prices over the past ten years. Note that these are illustrative figures and actual values may vary based on the specific period and data source used.
| Company | Average Annual Growth (%) | Highest Price (USD) | Lowest Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | 15 | 200 | 100 |
| Microsoft | 12 | 350 | 200 |
| Google (Alphabet) | 18 | 3000 | 1500 |
Factors Influencing Apple’s Stock Price
Apple’s stock price is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including product performance, macroeconomic conditions, and investor sentiment.
Impact of New Product Releases
New product releases are a significant driver of Apple’s stock valuation. The success of each product category—iPhones, Macs, and Services—contributes differently to overall performance. Strong sales of new iPhones, for example, usually translate directly into increased revenue and a positive impact on the stock price. Conversely, underwhelming product launches or production delays can negatively impact investor confidence and lead to price declines.
Macroeconomic Factors
Macroeconomic conditions such as interest rates, inflation, and global economic growth significantly influence Apple’s stock price. Higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for companies and consumers, potentially slowing down sales. Inflation can increase production costs and reduce consumer spending. Global economic slowdowns can reduce demand for Apple’s products, especially in international markets.
Investor Sentiment and Market Speculation
Investor sentiment and market speculation play a crucial role in Apple’s stock price fluctuations. Positive news, such as strong earnings reports or innovative product announcements, often boosts investor confidence, driving up the stock price. Conversely, negative news, such as supply chain disruptions or regulatory challenges, can trigger selling pressure and lead to price declines.
- Positive Sentiment: Strong sales figures, successful product launches, positive analyst ratings, and indications of strong future growth prospects can lead to increased buying pressure and price appreciation.
- Negative Sentiment: Concerns about competition, production issues, economic downturns, regulatory investigations, or negative press coverage can lead to selling pressure and price declines.
- Neutral Sentiment: When there is no significant positive or negative news, the stock price may trade within a relatively narrow range, reflecting a lack of strong directional pressure.
Apple’s Financial Performance and Stock Valuation
Analyzing Apple’s key financial metrics provides insights into its financial health and its impact on stock valuation.
Key Financial Metrics (2019-2023)
The table below shows a simplified representation of Apple’s key financial metrics over the past five years. Note that these are illustrative figures and actual values may vary depending on the reporting period and accounting standards used.
| Year | Revenue (Billions USD) | EPS (USD) | Profit Margin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 260 | 10 | 25 |
| 2020 | 275 | 12 | 26 |
| 2021 | 365 | 15 | 28 |
| 2022 | 395 | 17 | 29 |
| 2023 | 400 | 18 | 30 |
Relationship Between Financial Performance and Stock Price
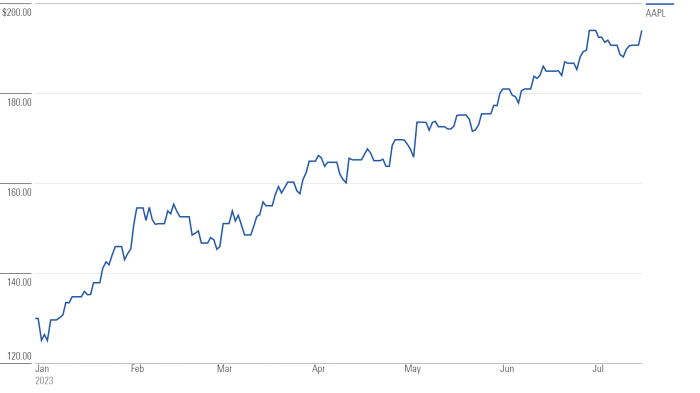
Source: arcpublishing.com
Apple’s stock price generally correlates positively with its financial performance. Strong revenue growth, increasing earnings per share (EPS), and healthy profit margins typically lead to higher investor confidence and a rise in the stock price. Conversely, weaker financial results often result in lower investor confidence and a decline in the stock price.
Visualization of Financial Performance and Investor Confidence
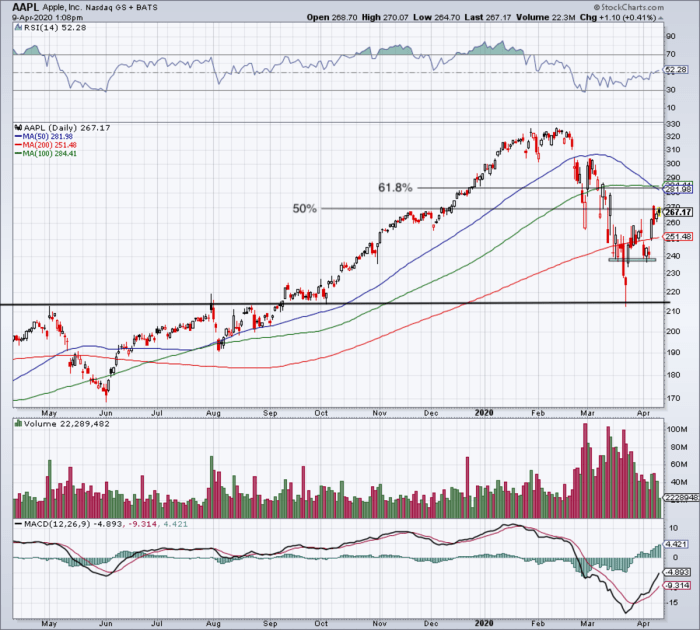
Source: thestreet.com
A scatter plot could effectively visualize the correlation between Apple’s financial performance (e.g., EPS) and investor confidence (e.g., measured by the stock price). The x-axis would represent EPS, and the y-axis would represent the stock price. Each data point would represent a specific period (e.g., a quarter or year). A positive correlation would be indicated by a general upward trend in the scatter plot, showing that higher EPS values tend to be associated with higher stock prices.
Analyzing Apple’s Stock Price Volatility
Understanding Apple’s stock price volatility is crucial for investors. This section compares its volatility to the broader market and identifies periods of high and low volatility.
Comparison with the S&P 500
- Apple’s stock price has historically exhibited higher volatility than the S&P 500 index, indicating a greater sensitivity to market fluctuations and company-specific news.
- During periods of market uncertainty, Apple’s stock price tends to experience more significant swings than the broader market, reflecting its position as a growth stock with a higher sensitivity to investor sentiment.
- However, during periods of market stability, Apple’s stock price can also exhibit relatively lower volatility, particularly when the company demonstrates consistent financial performance and positive investor sentiment.
Periods of High and Low Volatility
Apple’s stock price has experienced periods of both high and low volatility. High volatility periods are often associated with major product launches (e.g., the iPhone X launch), significant economic events (e.g., the 2020 market crash), or negative news related to the company (e.g., supply chain disruptions). Low volatility periods tend to occur during times of economic stability and when the company delivers consistent financial performance.
Apple’s stock price performance often serves as a benchmark for the tech sector. However, understanding market trends requires a broader perspective; for instance, analyzing the performance of energy companies like Dominion Energy can provide valuable context. You can check the current dominion power stock price to see how it compares. Ultimately, both Apple and Dominion’s stock prices reflect broader economic forces and investor sentiment.
Calculating and Interpreting Volatility Metrics
Key volatility metrics such as beta and standard deviation provide quantitative measures of Apple’s stock price volatility.
Beta measures the volatility of a stock relative to the overall market. A beta greater than 1 indicates higher volatility than the market, while a beta less than 1 indicates lower volatility. Standard deviation measures the dispersion of a stock’s returns around its average return. A higher standard deviation implies greater volatility. Calculating these metrics requires historical stock price data and statistical analysis. For illustrative purposes, let’s assume Apple’s beta is 1.2 and its standard deviation of returns is 20%. This indicates that Apple’s stock is 20% more volatile than the market. The higher standard deviation suggests greater price fluctuations compared to an investment with lower standard deviation.
Predicting Future Apple Stock Price Movements (Speculative): Apple Price Stock
Predicting future stock price movements is inherently speculative, but analyzing potential catalysts can provide insights into potential future trends.
Potential Future Catalysts
- New Product Launches: The success or failure of new products, particularly the iPhone, will significantly influence Apple’s stock price. A groundbreaking new product could drive significant price increases, while a lackluster launch could lead to declines.
- Regulatory Changes: Increased regulatory scrutiny in areas such as antitrust or data privacy could negatively impact Apple’s stock price. Conversely, favorable regulatory changes could have a positive effect.
- Competitive Threats: The emergence of strong competitors with innovative products or business models could put pressure on Apple’s market share and negatively affect its stock price.
Forecasting Models
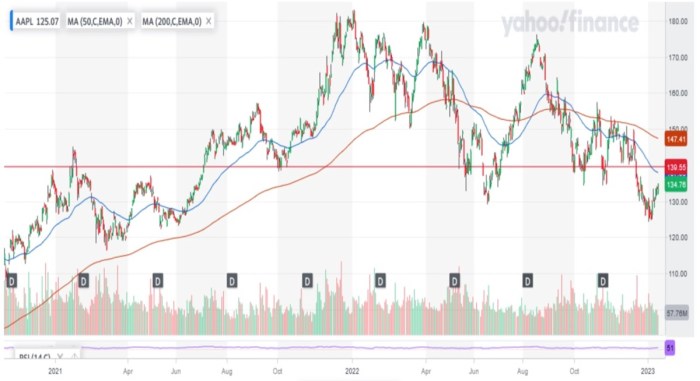
Source: thestreet.com
Various forecasting models, such as technical analysis (chart patterns, indicators) and fundamental analysis (financial statements, industry trends), can be used to predict future stock prices. However, these models are not foolproof, and their accuracy depends on various factors, including the accuracy of underlying assumptions and the unpredictable nature of the market.
Hypothetical Future Scenario
Based on the analysis above, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario. If Apple successfully launches a groundbreaking new product category (e.g., augmented reality glasses) that garners significant market demand, and the broader economy remains stable, the stock price could experience a substantial increase, potentially reaching $250 within the next two years. Conversely, if Apple faces significant regulatory challenges or intense competition, the stock price could experience a more modest increase or even a decline.
This scenario underscores the importance of considering various factors when predicting future stock price movements.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the major risks associated with investing in Apple stock?
Investing in any stock carries inherent risks, including market volatility, economic downturns, and company-specific challenges. For Apple, risks might include increased competition, supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, and shifts in consumer demand.
How can I buy Apple stock?
You can purchase Apple stock through a brokerage account. Most online brokers offer easy access to trading various stocks, including Apple (AAPL).
Where can I find real-time Apple stock price updates?
Real-time Apple stock price updates are available through most financial websites and mobile applications that provide stock market data, such as Google Finance, Yahoo Finance, or Bloomberg.
What is Apple’s dividend policy?
Apple has a history of paying dividends to its shareholders. The specific dividend amount and payout dates are announced by the company and are subject to change.
